Shapes are everywhere around us! When you look at the sun, it looks like a circle. A door looks like a rectangle. A ball looks like a sphere.
If your child enjoys identifying shapes, take the next step by exploring spatial understanding for Class 1
Learning shapes helps children:
- Recognize objects in daily life
- Build early math and geometry skills
- Improve observation and problem-solving
That’s why shapes for Grade 1 are taught in a simple, fun, and visual way.
Math contests like the Math Kangaroo also test basic spatial and shape recognition.
What are shapes?
In Mathematics, geometrical shapes are the figures that show the form or outline of the objects we see in our everyday life. In geometry, shapes are the forms of objects that have boundary lines, angles, and surfaces.
Types of Geometrical Shapes in Math
In geometry, shapes are grouped into two main categories: 2D shapes and 3D shapes.
2D (Two-Dimensional) Shapes
A two-dimensional, or 2D, object is a flat object that has length and width but no depth.
These are flat figures that we can draw on paper. They have only length and width, but no depth.
Examples: circle, square, rectangle, triangle, oval.
2D (two-dimensional) Shapes Types
2D shapes are flat figures that have only length and width. They can be drawn on paper and are also called plane shapes.
Some common 2D Shapes are:
Square: A square has four equal sides and four corners. All sides are the same length, and the corners (called vertices) are right angles (90 degrees).
Example: A chessboard or some windows are shaped like squares.
Rectangle: A rectangle has four sides with opposite sides equal in length. It also has four corners, all right angles.
Example: A door or a book cover is usually shaped like a rectangle.
Triangle: A triangle has three sides and three corners. The sides can be the same length or different lengths.
Example: The roof of a house or a slice of pizza.
Circle: A circle has no sides or corners. It is a round shape with a continuous curve.
Example: A clock face or a coin.
Parallelogram: A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides and opposite angles are equal in measure.
Example: A rectangle (like a door or notebook paper) is a parallelogram because its opposite sides are parallel and equal.
Polygons: These are made up of line segments and no curves. They are enclosed structures based on different lengths of sides and different angles.
Example:Pentagon (5 sides): A home plate in baseball
3D (Three-Dimensional) Shapes
A three-dimensional, or 3D, object has length, width, and depth.
These are solid figures that we can hold or touch. They have length, width, and height (or depth).
Examples: cube, cuboid, sphere, cone, cylinder.
3D (three-dimensional) Shapes Types
3D shapes are solid figures. They have length, width, and height (or depth). Unlike 2D shapes, they take up space and can be touched.
Cube: A cube is a three-dimensional shape which has 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges. The faces of the cube are square.
Example of Cube
Cuboid: A cuboid is also three dimensional solid having 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges but the faces of the cuboid are in a rectangular shape.
Example of Cubold
Cone: A cone is a solid which has a circular base and narrows smoothly from the surface to the top at a point called apex or vertex.
Example of Cone
Cylinder: A cylinder is a 3d solid shape that has two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. It has no vertex.
Example of Cylinder
Sphere: A sphere is a round shape in a 3d plane, whose radius is extended to three dimensions (x-axis, y-axis and z-axis).
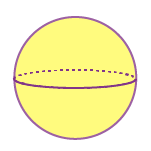
Example of Sphere
Basic Shapes for Grade 1: Circle, Square, Rectangle, Triangle
Learning about basic geometrical shapes is one of the first steps in Grade 1 math. Shapes help children understand the world around them, recognize patterns, and build a strong foundation for geometry.
Older students can develop these logical skills through Junior Math Olympiad preparation
Here are the most common 2D shapes every child should know:
Square
- Has 4 equal sides.
- Has 4 corners (also called vertices).
- Example in real life: a window, a chessboard, or a dice face.
A square is a box shape where all sides are the same.
Rectangle
- Has 4 sides.
- Opposite sides are equal in length.
- Has 4 corners.
- Example in real life: a door, a book cover, or a mobile screen.
A rectangle looks like a long box shape.
Triangle
- Has 3 sides.
- Has 3 corners.
- Example in real life: a pizza slice, a roof top, or a traffic sign.
A triangle is a three-sided shape that can look tall, wide, or flat depending on its angles.
Circle
- Has no sides and no corners.
- It is perfectly round and curved all around.
- Example in real life: a clock, a coin, or the sun.
A circle is the round shape we see in wheels, plates, and balls.
There are 4 basic shapes that we see everywhere. These shapes are:

You can find these shapes in all sorts of objects.

As you can see, these four basic shapes can be found everywhere.
Identify Rectangles, Squares, Circles, and Triangles
Recognizing shapes means being able to see and name the shapes we find around us every day. Sorting shapes means grouping them based on their features, such as the number of sides or whether the sides are straight or curved.
Let’s learn how to identify these simple shapes and find them around you.
We will start with circles. Circles are round, just like this ball.
Many things are shaped like a circle.

Look around and see what circles you can find.
Next is a triangle. A triangle has three sides.
Here are some other things that are shaped like a triangle.
What can you find that is shaped like a triangle?
On to squares and rectangles. They both have four sides.
Squares have sides that are all the same length.
Rectangles have two pairs of equal sides.

As you can see, there are a lot of things that are shaped like squares and rectangles.
Properties of Shapes
Shapes are special because they have different parts, called properties. These help us tell one shape from another.
- Sides → the straight or curved lines of a shape
- Example: A triangle has 3 sides.
- Corners (Vertices) → the points where two sides meet
- Example: A square has 4 corners.
- Edges → the lines between two faces (only in 3D shapes)
- Example: A cube has 12 edges.
- Faces → the flat surfaces of solid (3D) shapes
- Example: A cube has 6 faces.
How to Make Learning Shapes Fun for First Graders
There are many simple and fun ways you can help your child understand geometrical shapes at home. Everyday objects, games, and activities make learning exciting and meaningful.
To strengthen problem-solving skills early, explore free Math Olympiad training resources online
1. Spot Shapes Around You
Encourage your child to identify 2D and 3D shapes in real life.
- Look for 2D shapes in patterns on curtains, tiles, or book illustrations.
- Explain that 2D shapes are flat, while 3D shapes are solid. For example, a coin looks flat but is really a cylinder because it has height.
- Relate objects to 3D shapes:
- A ball is a sphere
- A cereal box is a cuboid
- A can is a cylinder
Activity: Find and circle hidden shapes in a picture.
2. Use Shape Language
When talking about shapes, use the correct mathematical terms.
- Remind your child that there is no shape called a diamond; instead, it could be a square, rhombus, or kite.
- Let your child touch and explore objects like a cereal box (cuboid) or a can (cylinder). Ask them to describe:
- Straight or curved edges
- Flat or curved faces
- Number of corners (vertices)
Example: “This cereal box is a cuboid. It has six faces, twelve edges, and eight corners.”
Compare two shapes (e.g., cube vs. cylinder) and talk about similarities and differences.
3. Play “Guess the Shape”
Turn shape learning into a game!
- Hide a shape in a bag.
- Ask your child to feel and describe it (edges, faces, corners).
- Let them guess the shape, then take it out to check.
Another version: Think of a shape and let your child ask yes/no questions until they figure it out.
This helps children visualize and reason about shapes—an important geometry skill.
4. Play “Find the Object” with Directions
Use position and direction words in daily play.
- Hide an object and encourage your child to ask:
- “Is it inside the drawer?”
- “If I move backwards, am I closer?”
- Practice turns (whole, half, quarter, three-quarter) to build an early sense of angles and rotation.
Words to use: left, right, in front, behind, between, near, far, above, below, inside, outside.
5. Practice with the Gonit App
For extra fun and practice, try the Gonit app. It has:
- Interactive geometrical shape games
- Worksheets and quizzes for Grade 1 geometry
- Activities that connect real-life objects to 2D and 3D shapes
With Gonit, children can learn shapes step by step, improve their math skills, and enjoy playful challenges at home or on the go. Practicing with fun activities and games helps children build a strong math foundation.
Final Thoughts on Geometrical Shapes for Grade 1
Geometrical shapes are the building blocks of mathematics. When children learn about shapes in Grade 1, they begin to understand how objects are formed, described, and connected to the real world. With the right guidance at school and practice at home, learning shapes becomes not only educational but also fun and memorable.